Accounting Acronyms Debits And Credits
Quiz 3: Debits and Credits Quiz. Test your knowledge of debits and credits with our online debits and credits quiz. Goods are bought on credit for 300, is the entry to the purchases account a debit or a credit? Credit Wrong. Cash is introduced to a business by the owner as equity. Which account does the credit entry go to?
Site Navigation. Have you ever walked blissfully unaware into a conversation about a recent pop-culture event you managed to miss?
Kotor 2 side quests. You probably spent most of your time smiling and trying to fake your way through it as others are throwing around unfamiliar terms and references.Not a fun experience.This uncomfortable feeling can be replicated in any industry. Knowing the lingo is an entry-point into the inner circle—an indicator that you truly belong. So if you’re starting to think about, your first step is to familiarize yourself with some of the basic accounting terms, acronyms and abbreviations out there.Because of the, different and these industry terms, it’s not uncommon for people to think working in accounting is inaccessible when really it just has its own unique language.
Knowing how to “talk the talk” will allow you to quickly shift your focus in the classroom beyond accounting terms and toward the techniques you’ll use in an accounting career.It's time to roll up those sleeves and build your accounting vocabulary. To help with this, we've compiled an assortment of basic financial terms and acronyms and created a simple accounting glossary for beginners. Basic accounting terms, acronyms, abbreviations and concepts to rememberCheck out these basic terms and start to commit them to memory. That way, when you start your degree journey, you’ll already feel like you’re a step ahead and speaking the language.
Accounts receivable (AR)Accounts receivable (AR) definition: The amount of money owed by customers or clients to a business after goods or services have been delivered and/or used. Accounting (ACCG)Accounting (ACCG) definition: A systematic way of recording and reporting financial transactions for a business or organization. Accounts payable (AP)Accounts payable (AP) definition: The amount of money a company owes creditors (suppliers, etc.) in return for goods and/or services they have delivered. Assets (fixed and current) (FA, CA)Assets (fixed and current) definition: Current assets (CA) are those that will be converted to cash within one year. Typically, this could be cash, inventory or accounts receivable. Fixed assets (FA) are long-term and will likely provide benefits to a company for more than one year, such as a real estate, land or major machinery.
Asset classesAsset class definition: An asset class is a group of securities that behaves similarly in the marketplace. The three main asset classes are equities or stocks, fixed income or bonds, and cash equivalents or money market instruments.
Balance sheet (BS)Balance sheet (BS) definition: A financial report that summarizes a company's assets (what it owns), liabilities (what it owes) and owner or shareholder equity;at a given time. Capital (CAP)Capital (CAP) definition: A financial asset or the value of a financial asset, such as cash or goods. Working capital is calculated by taking your current assets subtracted from current liabilities—basically the money or assets an organization can put to work.
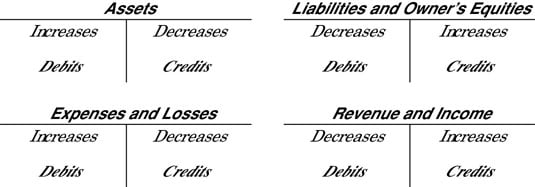
Cash flow (CF)Cash flow (CF) definition: The revenue or expense expected to be generated through business activities (sales, manufacturing, etc.) over a period of time. Certified public accountant (CPA)Certified public accountant (CPA) definition: A designation given to an accountant who has passed a standardized and met government-mandated work experience and educational requirements to. Cost of goods sold (COGS)Cost of goods sold (COGS) definition: The direct expenses related to producing the goods sold by a business. The formula for calculating this will depend on what is being produced, but as an example this may include the cost of the raw materials (parts) and the amount of employee labor used in production. Credit (CR)Credit (CR) definition: An accounting entry that may either decrease assets or increase liabilities and equity on the company's balance sheet, depending on the transaction.
When using the there will be two recorded entries for every transaction: A credit and a debit. Debit (DR)Debit (DR) definition: An accounting entry where there is either an increase in assets or a decrease in liabilities on a company's balance sheet. DiversificationDiversification definition: The process of allocating or spreading capital investments into varied assets to avoid over-exposure to risk. Enrolled agent (EA)Enrolled agent (EA) definition: A tax professional who represents taxpayers in matters where they are dealing with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). This piece of ad content was created by Rasmussen College to support its educational programs. Rasmussen College may not prepare students for all positions featured within this content.
Please visit for a list of programs offered. External links provided on rasmussen.edu are for reference only. Rasmussen College does not guarantee, approve, control, or specifically endorse the information or products available on websites linked to, and is not endorsed by website owners, authors and/or organizations referenced.
Rasmussen College is a regionally accredited private college.
Site Navigation. Have you ever walked blissfully unaware into a conversation about a recent pop-culture event you managed to miss?
You probably spent most of your time smiling and trying to fake your way through it as others are throwing around unfamiliar terms and references.Not a fun experience.This uncomfortable feeling can be replicated in any industry. Knowing the lingo is an entry-point into the inner circle—an indicator that you truly belong.
So if you’re starting to think about, your first step is to familiarize yourself with some of the basic accounting terms, acronyms and abbreviations out there.Because of the, different and these industry terms, it’s not uncommon for people to think working in accounting is inaccessible when really it just has its own unique language. Knowing how to “talk the talk” will allow you to quickly shift your focus in the classroom beyond accounting terms and toward the techniques you’ll use in an accounting career.It's time to roll up those sleeves and build your accounting vocabulary. To help with this, we've compiled an assortment of basic financial terms and acronyms and created a simple accounting glossary for beginners. Basic accounting terms, acronyms, abbreviations and concepts to rememberCheck out these basic terms and start to commit them to memory. That way, when you start your degree journey, you’ll already feel like you’re a step ahead and speaking the language.

Accounts receivable (AR)Accounts receivable (AR) definition: The amount of money owed by customers or clients to a business after goods or services have been delivered and/or used. Accounting (ACCG)Accounting (ACCG) definition: A systematic way of recording and reporting financial transactions for a business or organization. Accounts payable (AP)Accounts payable (AP) definition: The amount of money a company owes creditors (suppliers, etc.) in return for goods and/or services they have delivered. Assets (fixed and current) (FA, CA)Assets (fixed and current) definition: Current assets (CA) are those that will be converted to cash within one year. Typically, this could be cash, inventory or accounts receivable. Fixed assets (FA) are long-term and will likely provide benefits to a company for more than one year, such as a real estate, land or major machinery.
Asset classesAsset class definition: An asset class is a group of securities that behaves similarly in the marketplace. The three main asset classes are equities or stocks, fixed income or bonds, and cash equivalents or money market instruments. Balance sheet (BS)Balance sheet (BS) definition: A financial report that summarizes a company's assets (what it owns), liabilities (what it owes) and owner or shareholder equity;at a given time. Capital (CAP)Capital (CAP) definition: A financial asset or the value of a financial asset, such as cash or goods. Working capital is calculated by taking your current assets subtracted from current liabilities—basically the money or assets an organization can put to work. Cash flow (CF)Cash flow (CF) definition: The revenue or expense expected to be generated through business activities (sales, manufacturing, etc.) over a period of time. Certified public accountant (CPA)Certified public accountant (CPA) definition: A designation given to an accountant who has passed a standardized and met government-mandated work experience and educational requirements to.
Cost of goods sold (COGS)Cost of goods sold (COGS) definition: The direct expenses related to producing the goods sold by a business. The formula for calculating this will depend on what is being produced, but as an example this may include the cost of the raw materials (parts) and the amount of employee labor used in production. Credit (CR)Credit (CR) definition: An accounting entry that may either decrease assets or increase liabilities and equity on the company's balance sheet, depending on the transaction. When using the there will be two recorded entries for every transaction: A credit and a debit.
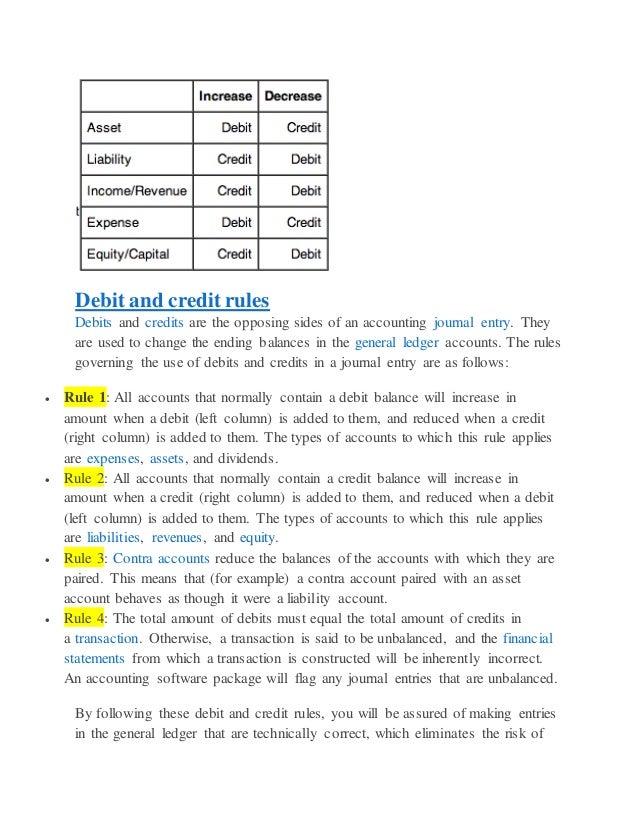
Debit (DR)Debit (DR) definition: An accounting entry where there is either an increase in assets or a decrease in liabilities on a company's balance sheet. DiversificationDiversification definition: The process of allocating or spreading capital investments into varied assets to avoid over-exposure to risk.
How Debit And Credit Work In Accounting
Enrolled agent (EA)Enrolled agent (EA) definition: A tax professional who represents taxpayers in matters where they are dealing with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). This piece of ad content was created by Rasmussen College to support its educational programs. Rasmussen College may not prepare students for all positions featured within this content. Please visit for a list of programs offered. External links provided on rasmussen.edu are for reference only.
Rasmussen College does not guarantee, approve, control, or specifically endorse the information or products available on websites linked to, and is not endorsed by website owners, authors and/or organizations referenced. Rasmussen College is a regionally accredited private college.